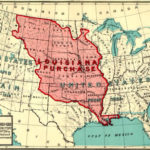
 In a ceremony on Dec. 20, 1803, the French turned Louisiana over to the United States at The Cabildo which was the seat of colonial government in New Orleans. By a treaty signed on Apr. 30, 1803, the United States purchased from France the Louisiana Territory, more than 2 million sq km (800,000 sq mi) of land extending from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains, which doubled America’s size. The price was 60 million francs, about $15 million; $11,250,000 was to be paid directly, with the balance to be covered by the assumption by the United States of French debts to American citizens.
In a ceremony on Dec. 20, 1803, the French turned Louisiana over to the United States at The Cabildo which was the seat of colonial government in New Orleans. By a treaty signed on Apr. 30, 1803, the United States purchased from France the Louisiana Territory, more than 2 million sq km (800,000 sq mi) of land extending from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains, which doubled America’s size. The price was 60 million francs, about $15 million; $11,250,000 was to be paid directly, with the balance to be covered by the assumption by the United States of French debts to American citizens.
In 1762, France had ceded Louisiana to Spain, but by the secret Treaty of San Ildefonso (1800) the French had regained the area. Napoleon Bonaparte (the future Emperor Napoleon I) envisioned a great French empire in the New World, and he hoped to use the Mississippi Valley as a food and trade center to supply the island of Hispaniola, which was to be the heart of this empire. First, however, he had to restore French control of Hispaniola, where Haitian slaves under TOUSSAINT L’OUVERTURE had seized power (1801; see HAITI). In 1802 a large army sent by Napoleon under his brother-in-law, Charles Leclerc, arrived on the island to suppress the Haitian rebellion. Despite some military success, the French lost thousands of soldiers, mainly to yellow fever, and Napoleon soon realized that Hispaniola must be abandoned. Without that island he had little use for Louisiana. Facing renewed war with Great Britain, he could not spare troops to defend the territory; he needed funds, moreover, to support his military ventures in Europe. Accordingly, in April 1803 he offered to sell Louisiana to the United States.
An enormous tract of land was now open to settlement, and the free navigation of the Mississippi was assured. Although the Constitution did not specifically empower the federal government to acquire new territory by treaty, Jefferson concluded that the practical benefits to the nation far outweighed the possible violation of the Constitution. The Senate concurred with this decision and voted ratification on Oct. 20, 1803. The Spanish, who had never given up physical possession of Louisiana to the French, reluctantly did so in an earlier ceremony at New Orleans on Nov. 30, 1803.